How Does Database Design Relate to the
SDLC?
What is SDLC?
According to Russell Kay, SDLC can be
defined as follows: System Development
Life Cycle (SDLC) is the overall process of developing information systems
through a multi-step process from investigation of initial requirements through
analysis, design, implementation and maintenance. There are many different
models and methodologies, but each generally consists of a series of defined
steps or stages. http://www.computerworld.com/developmenttopics/development/story/0,10801,71151,00.html
What are the steps involved in
SDLC?
As noted above, there
are numerous variations on the SDLC model, with each having iterative steps
such as planning, analysis, design, implementation, and maintenance. The following diagrams from Database
Systems: Design, Implementation, & Management, 5th Edition (Rob
& Coronel) illustrate one example of such a model.
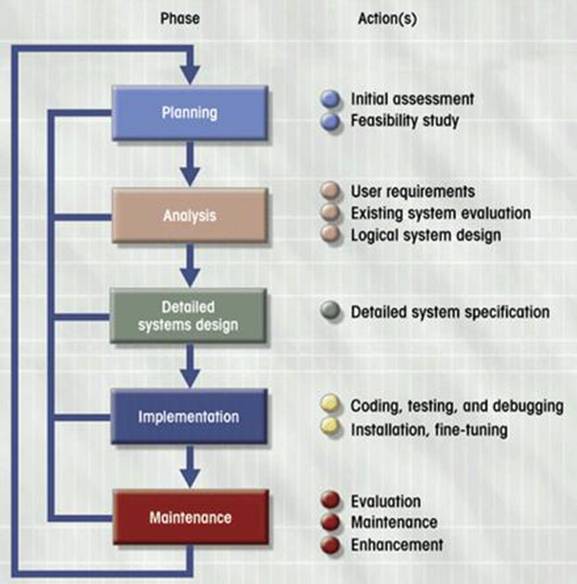
How does Database Design
Relate to the SDLC?
As a specific type of
information system, Database Design can be modeled using a similar SDLC type
approach, sometimes referred to as DBLC or the Database Development Life
Cycle. As in the SDLC approach, DBLC consists
of several iterative steps (which vary slightly depending on the model
used). However, the overall approach is
the same: A top down approach to
designing a database. Below is one model
of the DBLC.
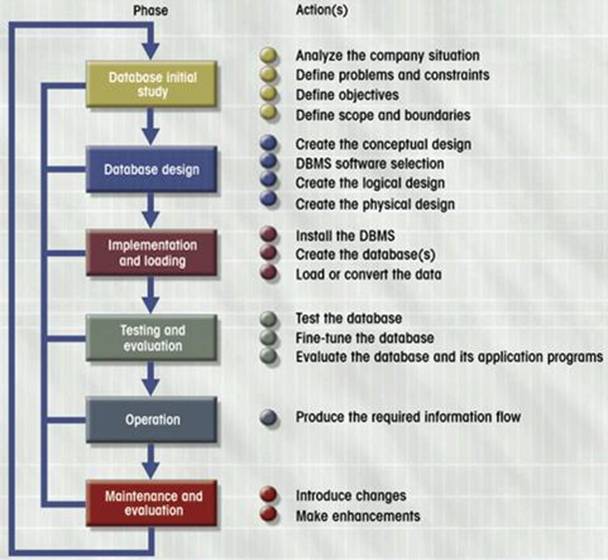
In Order to more fully understand the
DBLC, lets take a closer look at the separate stages in the process!
What takes place during the Database Initial Study?
This stage is
essentially the planning stage of the SDLC.
Purposes
Analyze company situation
Operating
environment
Organizational
structure
Define problems and constraints
Define objectives
Define scope and boundaries
What takes place during Database Design?
Alot! This stage encompasses much of both the Analysis and Design stages of the SDLC.
Most Critical
DBLC phase
Makes sure
final product meets requirements
Focus on data
requirements
Subphases
Create conceptual design
DBMS software selection
Create logical design
Create physical design
Since this is such a critical phase, lets break it down into the subphases defined above:
CONCEPTUAL DESIGN
Data modeling
creates abstract data structure to represent real-world items
High level of
abstraction
Four steps
Data analysis and requirements
Entity relationship modeling and normalization
Data model verification
Distributed database design
DBMS SOFTWARE SELECTION
DBMS software
selection is critical
Advantages and
disadvantages need study
Factors
affecting purchasing decision
Cost
DBMS features and tools
Underlying model
Portability
DBMS hardware requirements
CREATE LOGICAL DESIGN
Translates
conceptual design into internal model
Maps objects
in model to specific DBMS constructs
Design
components
Tables
Indexes
Views
Transactions
Access authorities
Others
CREATE PHYSICAL DESIGN
Creation of
special storage-related constructs
to house
end-user tables
Data loaded
into tables
Other issues
Performance
Security
Backup and recovery
Integrity
Company standards
Concurrency controls
As you can see, there is much work to do here!
What takes place during Implementation & Loading?
The efforts so far
are implemented!
Creation of special storage-related constructs
to house end-user tables
Data loaded into tables
Other issues
Performance
Security
Backup and
recovery
Integrity
Company
standards
Concurrency
controls
What takes place during Testing & Evaluation?
Make sure that the Database is working as planned!
Database is tested and fine-tuned for performance,
integrity, concurrent access, and security constraints
Done in parallel with application programming
Actions taken if tests fail
Fine-tuning
based on reference manuals
Modification
of physical design
Modification
of logical design
Upgrade or
change DBMS software or hardware
What takes place during Operation?
The Database is up
and running! Of course problems arise,
and changes are always necessary!
Database considered operational
Starts process of system evaluation
Unforeseen problems may surface
Demand for change is constant
What takes place during Maintenance & Evaluation?
Changes are made to the system as problems are solved and new requirements are identified.
In short, the process
begins anew!
Preventative
maintenance
Corrective
maintenance
Adaptive
maintenance
Assignment of
access permissions
Generation of
database access statistics to monitor performance
Periodic
security audits based on system-generated statistics
Periodic
system usage-summaries
In Summary:
There are a lot of steps
including many details not shown here!
The main thing to remember is
that the DBLC is a top-down approach to systematically implement and maintain a
database.
There is tons of information
on the Web detailing Database Design & the SDLC!
Some Useful References:
http://foe.mmu.edu.my/course/ecp3076/Lec6.ppt
http://cisnet.baruch.cuny.edu/holowczak/classes/4300/week2.html
http://courses.washington.edu/infosysb/class6-00-10-06.pdf
http://ourworld.compuserve.com/homepages/Peter_Koletzke/white_papers/imeth132.pdf
QUIZ
Now that we have looked at the DBLC in
great detail, its time to
test your knowledge!
Answer the following questions on a
sheet of paper, and then check above to see how you did!
Essay:
Define the SDLC.
Define the DBLC.
List the major steps involved in the SDLC.
List the major steps involved in the DBLC.
Identify 4 steps involved in the Design
phase.
Remember, the answer is above
.dont
cheat!
Multiple Choice:
Which of the following is not a step in SDLC?
A.
Planning
B.
Analysis
C.
Design
D.
Maintenance
E. All are part of SDLC
Which of the following tasks are included in
Conceptual Database Design?
A.
Data Analysis
B.
ERD Modeling
C.
Normalization
D.
Data Model Verification
E.
All of the above
Which of the following are considerations
when choosing a DBMS?
A.
Cost
B.
Features
C.
Portability
D.
Hardware Requirements
E.
All are Considerations
O.K., those should have been easy!!
The answer to each of the multiple
choice is E.
Congratulations! You have completed this tutorial.
Want to know even more about Databases?
Click on the link below for tons of
information.
http://calc.utep.edu/pkirs/mit5314/