
Let us start of by stating what a
linked list is. In simple terms a linked list is a chain of records
made up of two or more data types (either similar or dissimilar)
that will point to another record within the array. In fact there
are three types of linked lists. They are: single linked lists,
doubly linked lists, and circular linked lists.
A single linked list is linked in
one direction. This means that when sorting or performing a search
the list can only go one way.
A doubly linked list is linked in
two direction. Thus, when searching or sorting you can go in either
ascending or descending order.
Remember when creating linked
list the must always be a beginning and end to the list. A pointer
will be used to denote the begging of the list while the NULL
character will signify the end of the list.
However, a circular linked list
will not use the null character to denote the end of the list.
Instead the beginning address will be used to test where the list
ends. A circular linked list can be either single or double.
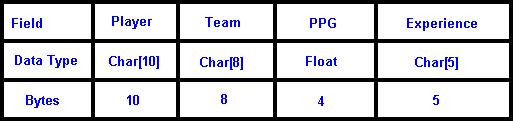
To have a conceptual view of the
different types of linked list we will first start off by
diagramming the table of the records we wish to store.
At runtime our records will be
given a base address. Thus, we can insert a pointer field to direct
us to the next record in our list.
Now with the addition of data,
and addresses given at run time our database will look like this:
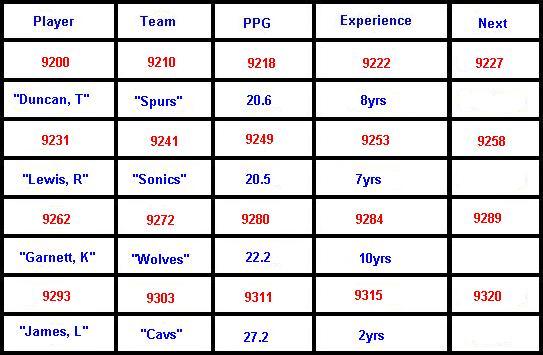
Note that the pointer field will
be designated as next.
Here is the conceptual view of
this linked list if we were to order the list by name:
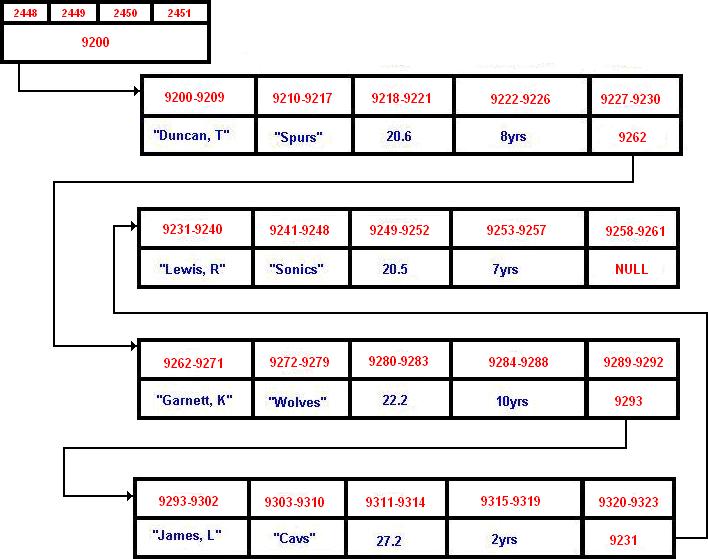
Remember that for each linked
list we must have a beginning and an end. The first pointer we
initialized will point to the first record on our list. In this
case our first pointer will point to the address 9200 which is first
on our list. Then, each record in our database will point to the
following record until we reach the NULL character which signifies
the end of the linked list.
This what a doubly linked list
would look like:
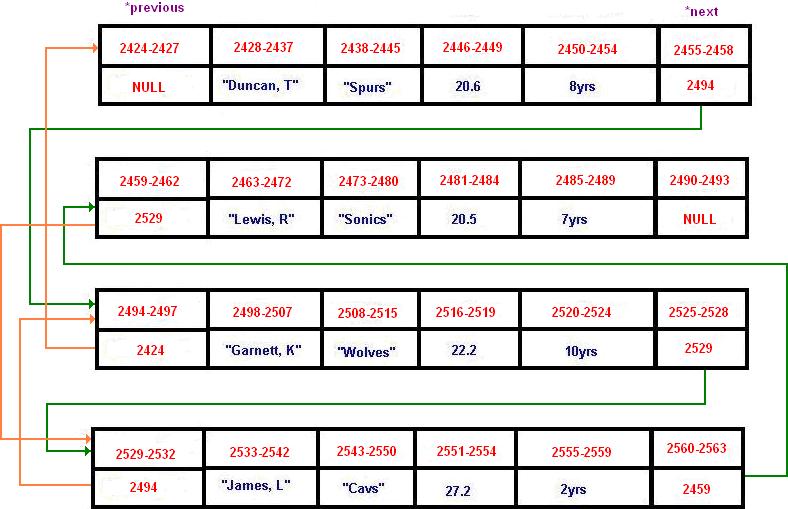
In this case we added an
additional pointer to search for the previous record as well.
Notice that linked list orders the player by name in both ascending
and descending order. Thus, the direction of the linked list goes
in two ways.
And now for the final conceptual
view of our linked list, the circular linked list:
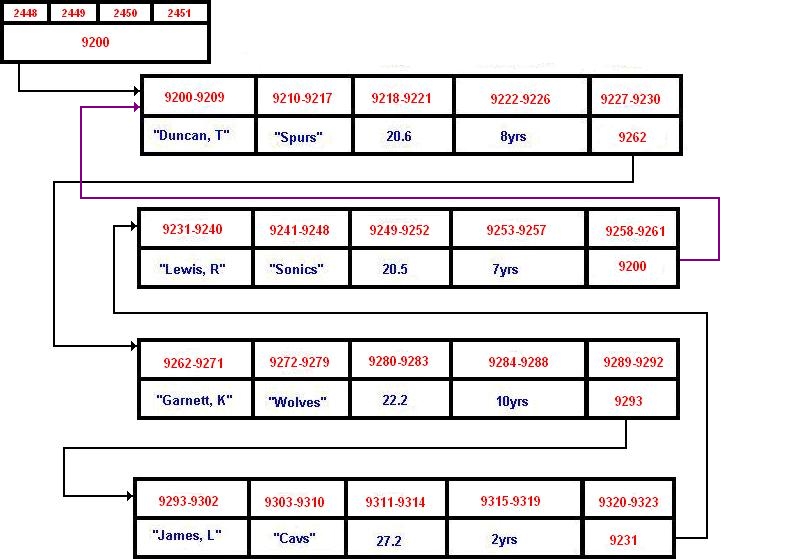
A circular linked list can be
both singular or double. This example is a circular single linked
list. This type of linked list is similar to the previous example
of our single linked list. However, the end is not denoted by the
NULL character. The end of the list is signified by the pointer
directing the list to where it began. Hence the name circular
linked list because it continues in loop.
Links of
Reference:
Link 1
Link 2
Link 3

 CIS3355:
Business Data Structures
CIS3355:
Business Data Structures