What
is an Array?
An Arrays a data structure that has a fixed number of contiguous
storage of all the same data types Arrays are also referred to
as matrices or a matrix. Arrays can also be multidimensional,
and have numerous elements.
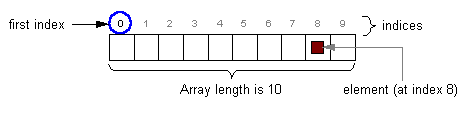
To find a position in an array we need to know the base address
and the number of the offset, or index. The elements in the
array are taking up a contiguous piece of memory so the elements
are sequential and take up two bytes each.
Questions:
1.- How can we create an array?
You use a new operator, plus the data type
of the array elements, plus the number of elements desired
enclosed within square brackets. The next statement in the
sample program allocates an array with enough memory for ten
integer elements and assigns the array to the variable an Array
declared earlier. int prime[10]={1,5,7,9,11,13,15,17,19,21,};h
2.- How can we access elements in an array?
The memory has been allocated for the array
at runtime, the program assigns values to the arrays elements.
The code shows the reference an array element, either to assign
a value to it, or to access the value, and the square brackets
to the array name. The value between the square brackets
indicates the index of the element to access.
3.- How can we know the size of an array?
To get the size of an array, you write
arrayname.length in the program
4.- How we declare an array in the
code? Answer: e
a) int [] an array;
b) like variable
c) array type
d) array name
e) all the above
5.- How many bytes needs a contiguously in
an array? Answer: a
a)2 bytes
b)4 bytes
c)8 bits
d)32 bits
References:
www.Java.sun.com
pweb.netcom.com/~tjensen/ptr/pointers.htm
Textbook on the webpage of www.pkirs.utep.edu/cis3355

 CIS3355:
Business Data Structures
CIS3355:
Business Data Structures