100.0120.D
int a = 1, b = 2, c = 3, d = 4, e = 5, f = 6, g = 7, h =
8, r1, r2, r3, r4, r7;
float v = 0.5, x = 1.0,
y = 2.0, z = 3.0, r5,
r6;
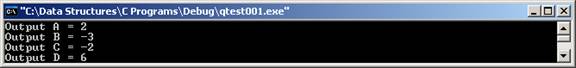
r1 = a + e/(e - b);
printf("Output A =
%d\n",r1
r2 = -b - (c + d) % b;
printf("Output B =
%d\n",r1);
r3 = a-- * b - ++c;
printf("Output C =
%d\n",r3);
r4 = c - a + e/b;
printf("Output D =
%d\n",r4);
WHY??
** REMEMBER: location/variable a = 0 and location c = 4 now.
c - a + e/b
= 4 – 0 + 5/2
= 4 – 0 + 2
= 4 + 2
= 6